Among these, the most likely ancestor of great apes and humans is probably Kenyapithecus or Griphopithecus. Humans and great apes are different from a common ancestor.
What was the last common ancestor between humans and chimpanzees?

The chimpanzee – human last common ancestor (CHLCA) is the last common ancestor shared by the Homo (human) and Pan (chimpanzee and bonobo) genera Hominini. This may interest you : How similar are humans to bananas?.
What was the last common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees when they were alive? These so -called hominoids – that is, gibbons, giant apes and humans – appeared and varied during the Miocene, about 23 million to 5 million years ago. (The last common ancestor found by humans and chimpanzees lived about 6 million to 7 million years ago.)
What ancestor did chimpanzees evolve from?
Among these, the most likely ancestor of great apes and humans is probably Kenyapithecus or Griphopithecus. On the same subject : What do we share the most DNA with?.
Where did chimpanzees originate from?
The chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes), also known as the chimp, is a species of large ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa.
Did chimpanzees evolve from human beings?
There is a simple answer: Humans did not evolve from chimpanzees or any other large monkeys alive today. Instead, we share a common ancestor who lived about 10 million years ago.
What is the common ancestor between humans and chimps?
Evidence from fossils, proteins and human studies suggests that humans and chimpanzees had a common ancestor millions of years ago. On the same subject : What do humans share the most DNA with?. Most scientists believe that the ‘human’ lineage (called the hominin sub-group) split from chimpanzees and other monkeys about five to seven million years ago.
What did chimps and humans evolve from?
5 to 8 million years ago. Soon, the tribe split into two different lineages. One of these lineages eventually evolved into gorillas and chimps, while the other evolved into ancient ancestors of humans called hominids.
What is the most recent common ancestor of chimpanzees and humans?
The chimpanzee – human last common ancestor (CHLCA) is the last common ancestor shared by the Homo (human) and Pan (chimpanzee and bonobo) genera Hominini.
What was the last common ancestor of monkeys and apes?
Saadanius hijazensis, a new species of invasive species that is closely related to monkeys and apes of the Old World.
What is the common ancestor of primates?
The evolutionary history of primates can be traced back 57-85/90 million years. One of the oldest known species as a primate-like mammal, Plesiadapis, originated in North America; the other, Archicebus, came from China.
What did monkeys and apes evolve from?
Monkeys evolved from humans during the Oligocene Epoch. Apes evolved from catarrhines in Africa during the Miocene Epoch. Apes are divided into small monkeys and large monkeys. Hominins include the elements that gave rise to our species, such as Australopithecus and H.
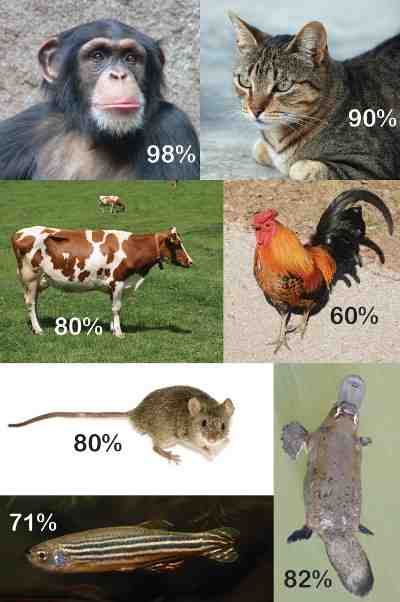
What percentage of DNA do humans share with bananas?
Well, no. In fact we share about 50% of our genes with plants – including bananas. “” Bananas have 44.1% of the same genetic makeup as humans. “
What do we share 50% of our DNA with? People share 50% of our DNA with a banana. Twenty -five percent of all your bones are in your legs. The average person walks the earth about three times in a lifetime.
How much DNA do we match with a banana?
Part of it, of course. Humans and bananas contain 40 to 60 percent of the same DNA. It doesn’t mean people are bananas or the other way around, but it does mean they have things in common. The DNA test took place during the National Human Genome Research Institute in 2013.
Do we share 99 of our DNA with bananas?
Well, no. In fact, we share about 50% of our genes with plants – including bananas.â € â € œBananas account for 44.1% of the genetic makeup of people.â €
Do humans really share 50 of their DNA with bananas?
So if a scientist looks at the DNA sequence of a banana and compares it to the DNA of a human it does not match. “You share 50 percent of your DNA with each of your parents. But with bananas, we share about 50 percent of our genes, which seems to be only 1 percent of our DNA,” honey said. Mike Francis, and Ph.D.
Do we share 1% of our DNA with bananas?
Even bananas surprisingly still share 60% of the same DNA as humans!
Do humans really share 50 of their DNA with bananas?
So if a scientist looks at the DNA sequence of a banana and compares it to the DNA of a human it does not match. “You share 50 percent of your DNA with each of your parents. But with bananas, we share about 50 percent of our genes, which seems to be only 1 percent of our DNA,” honey said. Mike Francis, and Ph.D.
Do we share 99 of our DNA with bananas?
Well, no. In fact, we share about 50% of our genes with plants – including bananas.â € â € œBananas account for 44.1% of the genetic makeup of people.â €
Do we share 50% of our DNA with a banana?
So if a scientist looks at the DNA sequence of a banana and compares it to the DNA of a human it does not match. “You share 50 percent of your DNA with each of your parents. But with bananas, we share about 50 percent of our genes, which seems to be only 1 percent of our DNA,” honey said. Mike Francis, and Ph.D.
What do we share 50% of our DNA with?
| Source | upusii |
|---|---|
| mirror.co.uk | â € œPeople share 50% of our DNA with a banana.â € |
| Internal Business | â € œThe gender equality between humans and bananas is 60 %.â € Source: National Human Genome Research Institute (However, it has nothing to do with when I tried to find out) |
What color was the first human being?

Color and cancer The skin of these ancient people may have been pale, like the closest human family, the chimpanzee, which is white under its fur. About 1.2 million to 1.8 million years ago, the onset of Homo sapiens caused the dark skin.
Can humans breed with any other animals?

Probably not. Traditional evaluations preclude definitive research on the subject, but it is safe to say that human DNA is so different from that of other animals that it may not be possible. her sexuality.
What happens when a person pairs with a chimpanzee? Humans and chimps have 95 percent identical DNA, and 99 percent of our DNA coding sequences are identical. However, there are 23 tubes of chromosomes in human DNA, while a chimp has only 22. The difference is that it is difficult to give birth to a healthy young, and they will not have children.
Did humans have a tail?

As it happens, we still have human tails – when we are conceived. Tails are a trait that can be traced back to the earth, so when a human embryo grows, we have shorter tails – including the vertebrae – in the early stages of our development, like all animals with bones.
When did the people lose their tails? The loss of the tail occurred about 25 million years ago, long before our species, Homo sapiens, walked the earth. Over the next several millions of years, the genetic playbook for tail development in our genealogy was obsolete, and all the components needed for tail growth have long been lost.
Why do humans no longer have tails?
Research shows that our ancestors lost their tails suddenly, rather than gradually, which is in line with scientific findings. in history. According to the research authors, the sudden change may have occurred in a single monkey about 20 million years ago, and passed on to offspring.
Do humans still have tails?
What causes human tails? To be clear, real human tails are very rare. They are often called old things or even “weird things” because of their rarity. It is also found twice in men than in women and is not inherited in families.
Why did humans stop having tails?
Recently, researchers found an example of why humans don’t have tails. They identified a phenomenon called the jump associated with the growth of the tail that may have jumped elsewhere in the genome of a primate species millions of years ago. And in doing so, a change was made that removed our tails.
Sources :
